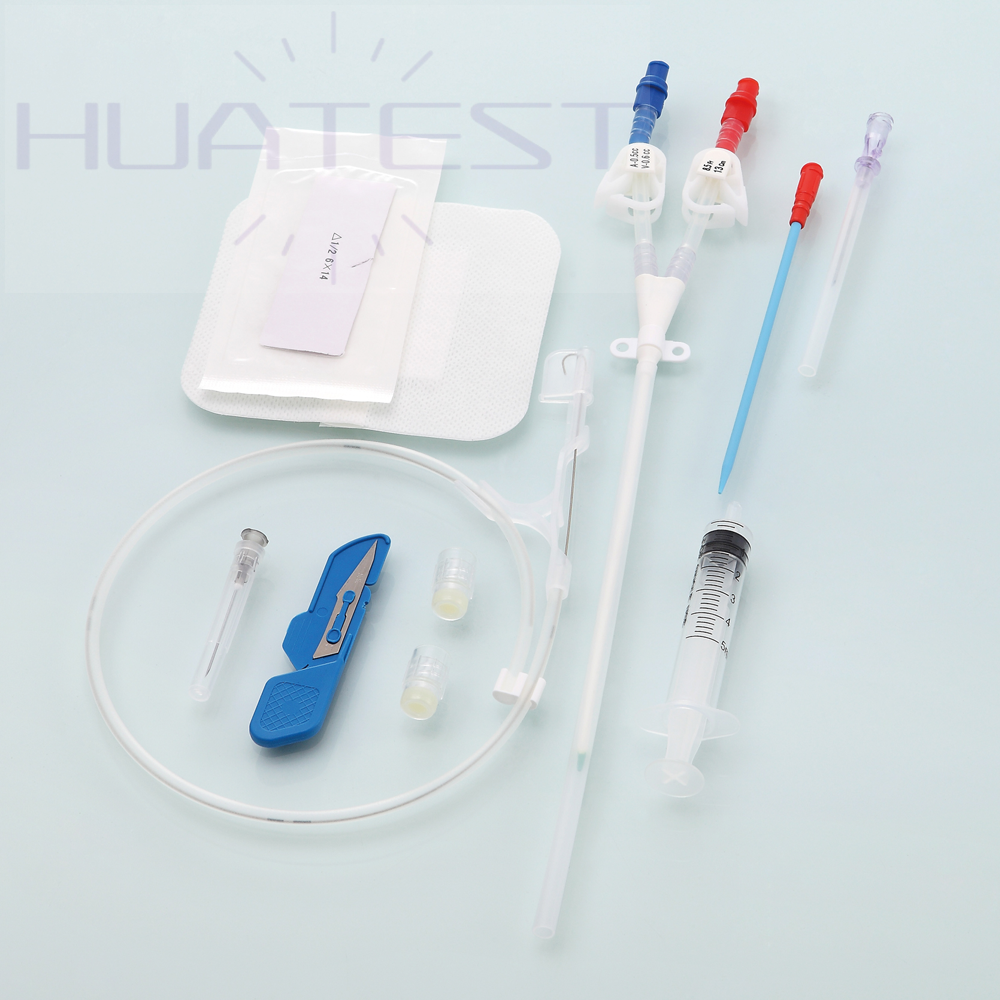
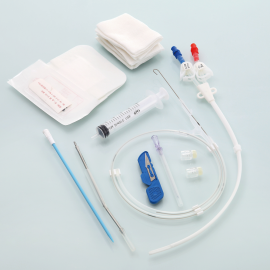
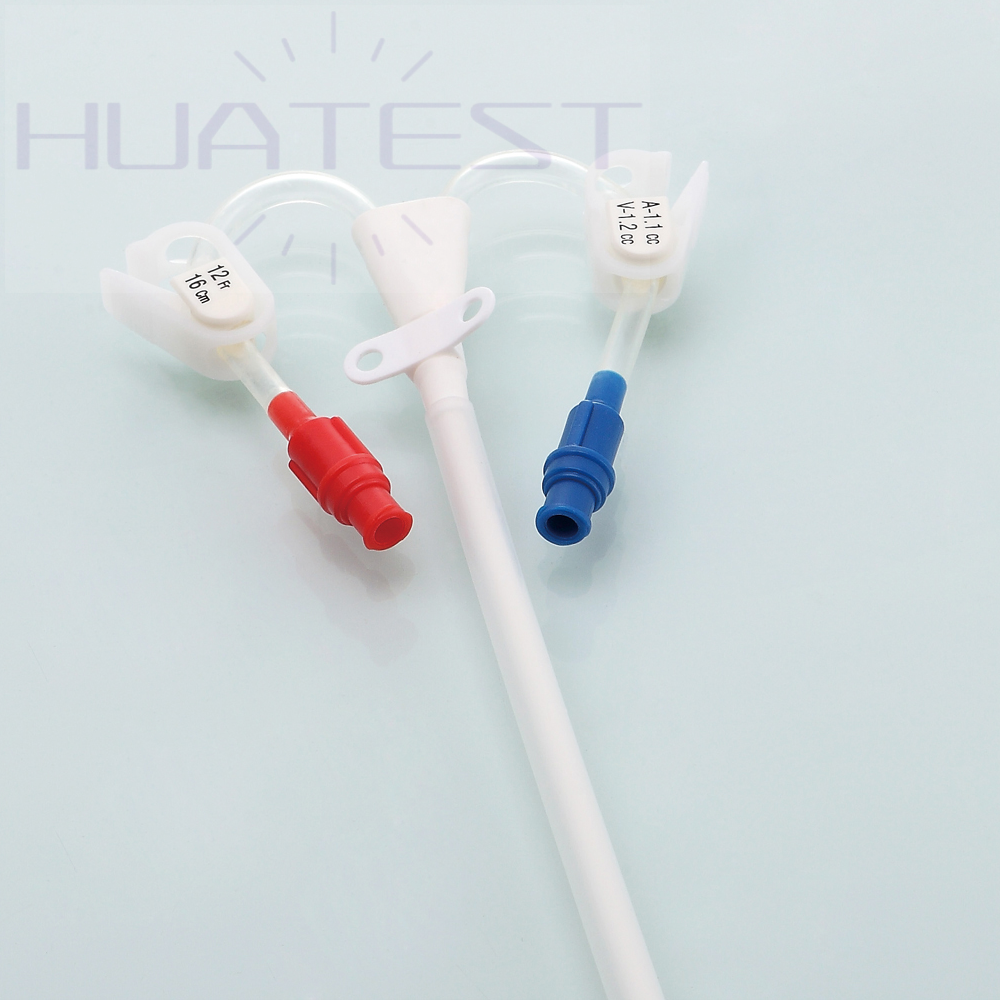
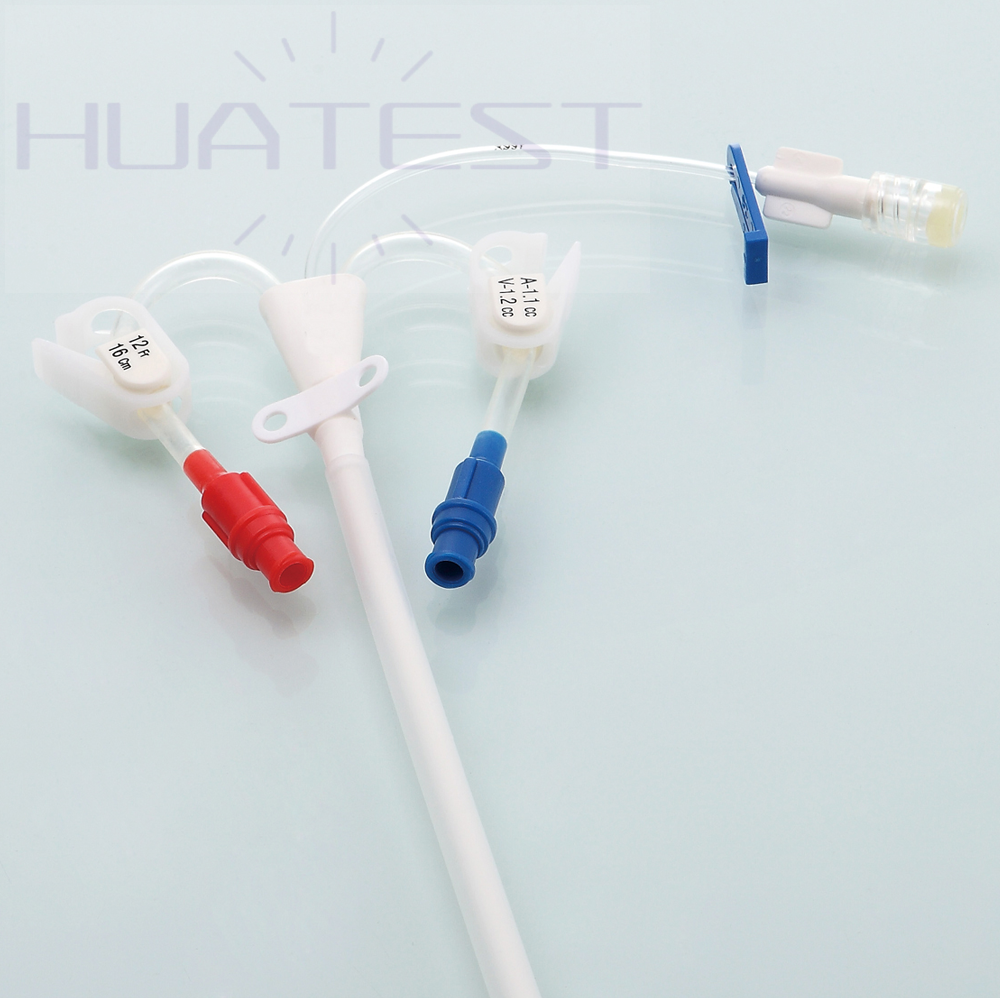
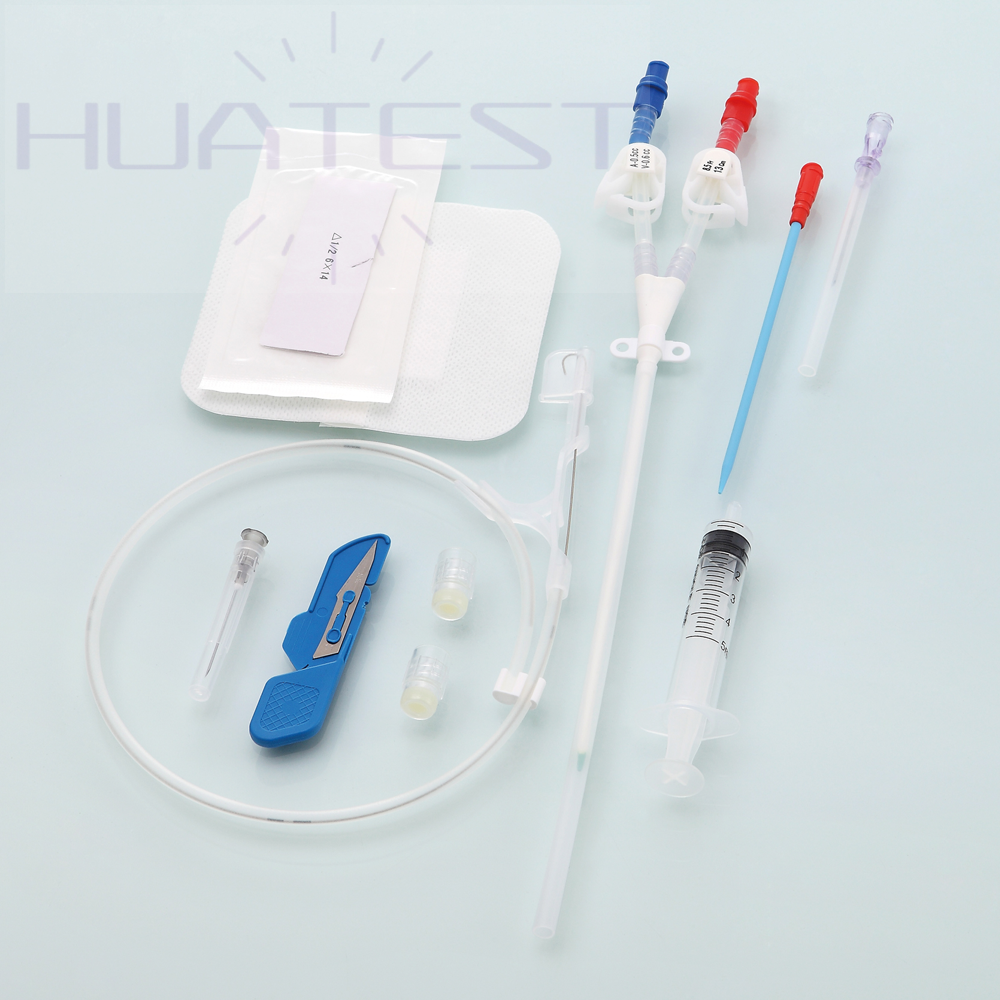
Double Lumen Hemodialysis Catheter
Double Lumen Hemodialysis Catheter
1. Dual-lumen design improves efficiency:
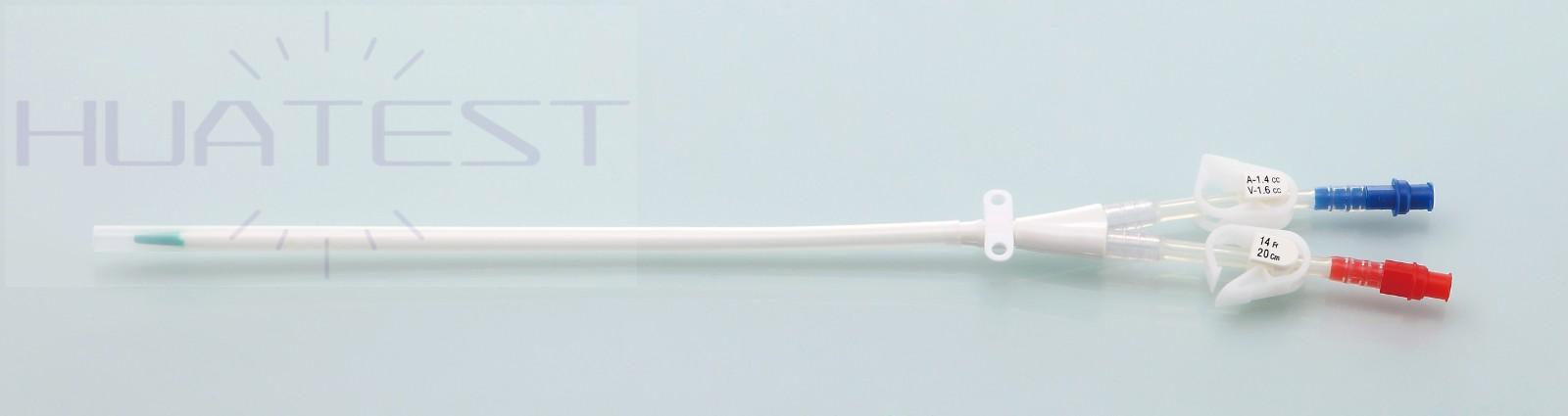
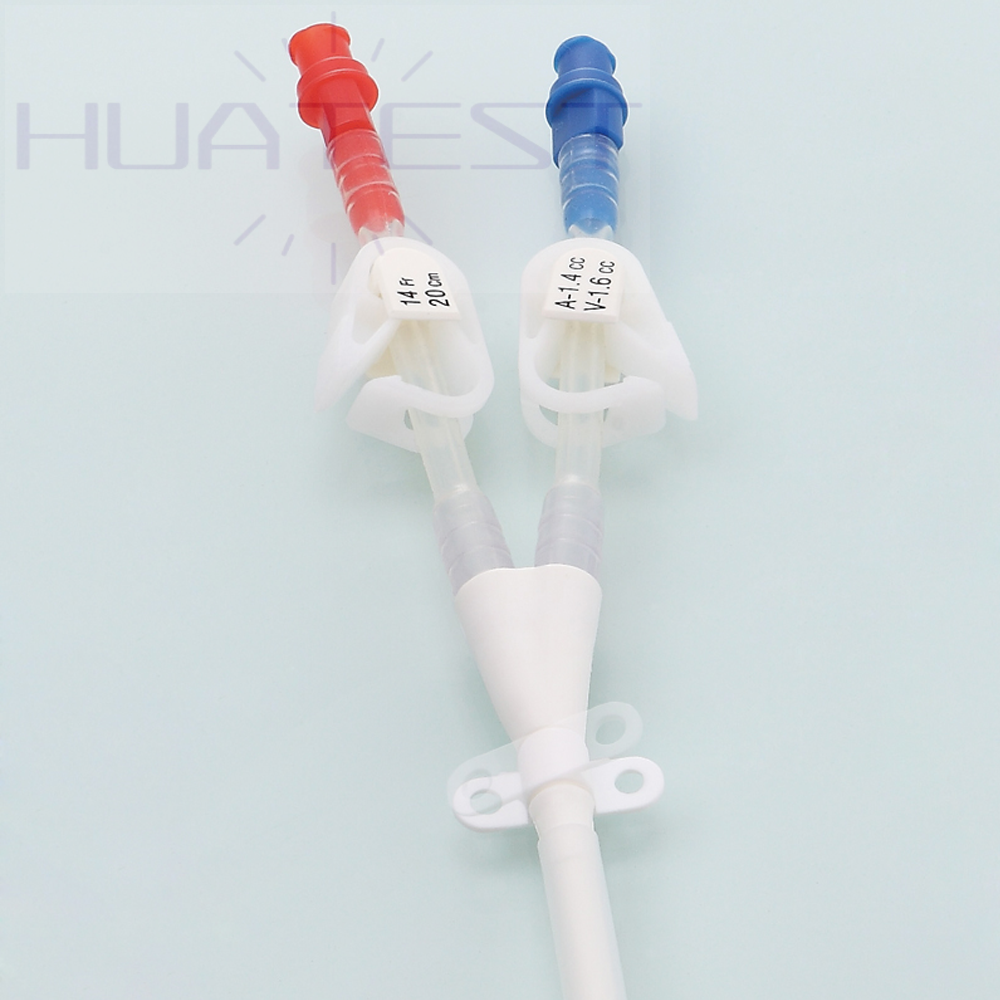
With a dual-lumen design, blood can be drawn out and reinfused in the catheter at the same time, ensuring the continuity and efficiency of the dialysis process. And the two independent chambers reduce the risk of blood reflux and mixing, which can improve the dialysis effect.
2. Adapt to a wide range of clinical needs:
Double Lumen Hemodialysis Catheter is suitable for patients with acute renal failure who need emergency dialysis, providing a long-term and stable dialysis access and reducing the need for frequent catheter replacement.
3. Multiple indications:
Suitable for patients who need high-flow hemodialysis to ensure that each dialysis can achieve the best effect. In the transition period before kidney transplantation, the double-lumen catheter provides patients with a reliable means of blood purification to ensure that their physical condition meets the surgical standards.
4. Easy operation and maintenance:
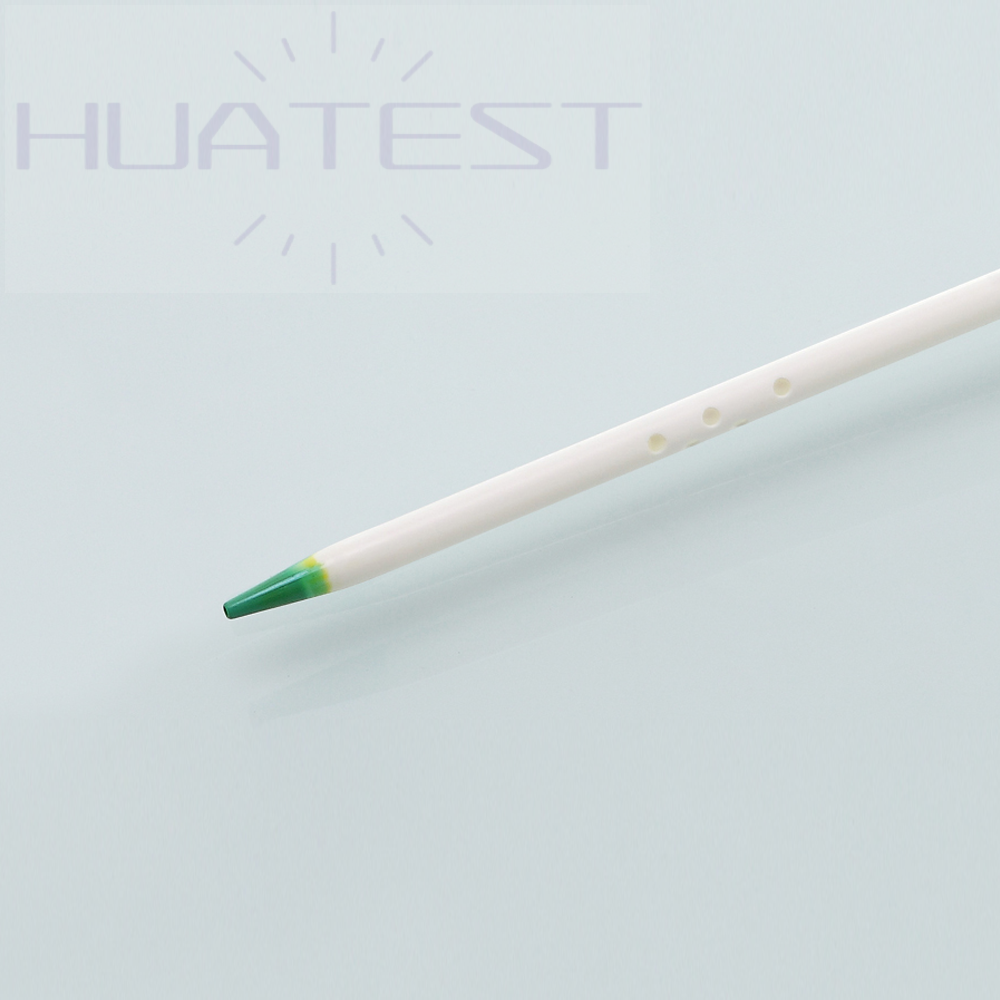
The catheter design is easy to insert and fix, which reduces the difficulty of operation and improves the convenience of clinical use. It also helps to reduce the risk of infection, makes maintenance easier, and prolongs the service life of the catheter.
5. Adapt to a variety of insertion sites:
According to the specific situation of the patient, the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein or femoral vein can be selected for insertion, providing a flexible clinical solution. The choice of various insertion positions improves the applicability of the catheter in different clinical environments.
6. High flow performance:
The inner diameter of the catheter is optimized to ensure high-flow hemodialysis needs and improve dialysis efficiency. Reduce dialysis time and improve the quality of life of patients.
Complications and Countermeasures
1. Infection: Maintain aseptic operation, change dressings and disinfect regularly, and use antibiotics for treatment.
2. Thrombosis: Use anticoagulants and flush the catheter regularly.
3. Catheter displacement or dislocation: Correctly fix the catheter to avoid excessive pulling.
4. Vascular injury: Insert carefully and use ultrasound guidance.
5. Air embolism: Ensure that the catheter is well sealed during the operation to prevent air from entering.
6. Stenosis: Monitor blood flow and perform vascular dilation if necessary.
7. Bleeding: Closely monitor bleeding and apply correct compression to stop bleeding.
8. Mechanical failure: Check the catheter function regularly and replace the catheter if necessary.



INQUIRY
CATEGORIES
LATEST NEWS
CONTACT US
Contact: Ms Sun Huaxing
Phone: +86 13806476056
E-mail: sales@huafengmedical.com
Whatsapp:+86 13806476056
Add: Room101,Bld 13,No.869 Huaguan Road,Qingdao China